- Home
- Health Center
- Health Info
- How can you prevent and treat indigestion?
How can you prevent and treat indigestion?


Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, is a common term used to describe a persistent or recurrent discomfort or pain felt in the upper abdomen just below the ribs.1 Discomfort refers to a subjective sensation such as upper abdominal fullness, early satiety, bloating, belching, nausea and vomiting.
Indigestion can be experienced by each person in different ways. So, the feeling of indigestion you feel might be slightly different from that of your friends. However, in most cases, indigestion is just mild and may only occur occasionally.
Symptoms of Indigestion
If you have indigestion, you may have:
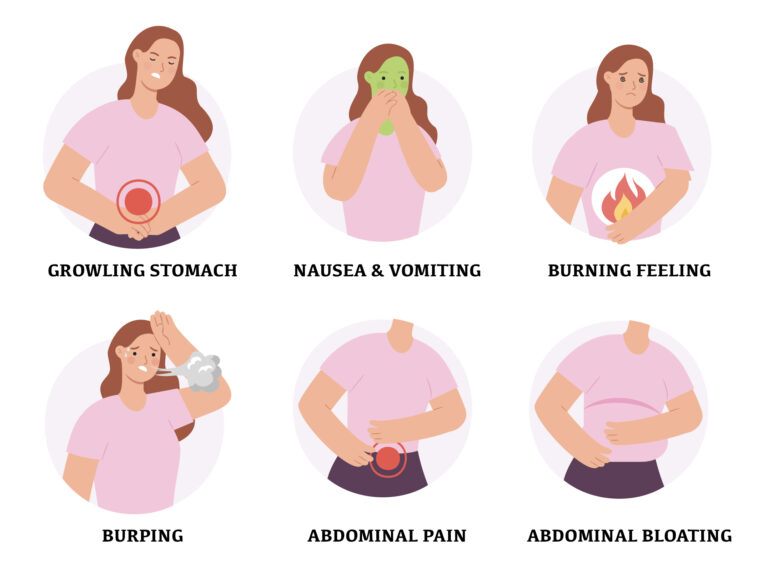
Causes of indigestion: 1
– Limit fried, spicy gassy foods
– Enjoy smaller portions
– Limit alcohol
– Quit smoking
– Wait an hour after eating to exercise
– Wear loose clothing
– Manage stress
– Manage your weight
– Avoid eating for a few hours before bed
There are many possible causes of indigestion. These can range from dietary and lifestyle habits to the side effects of medications and serious underlying conditions.
Lifestyles
– Overeating or eating too quickly
– Fatty, greasy or spicy foods
– Lying down soon after a meal
– Too much caffeine, alcohol, chocolate or carbonated beverages
– Cigarette smoking
– Anxiety or stress
Medications
– Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug (NSAID), such as aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen
– Certain antibiotics
– Thyroid medicines
Medical conditions
– Ulcers, GERD, Gastroparesis (a condition where stomach does not empty properly, often occurs in diabetes patient)
– Irritable bowel syndromes (IBS)
– Thyroid disease
– Pregnancy and obesity
How can you prevent and treat indigestion?3
Indigestion often goes away on its own and will pass with time. However, some lifestyle changes and medications can help you prevent and treat indigestion symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Medications:
If your indigestion persists, medications may help. Over-the-counter antacids(eg. Gaviscon Double Action) are generally the first choice. Other options include:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which can reduce stomach acid. PPIs may be recommended particularly if you experience heartburn along with indigestion.
- H2-receptor blockers, which can also reduce stomach acid.
- Prokinetics, which may be helpful if your stomach empties slowly.
- Probiotics 4 , which may help to restore gastric microbiota changes
*Proton pump inhibitors, H2-receptor blockers, prokinetics are controlled medications. Consult your pharmacist or doctor for further information.
When to see a doctor? 1
Mild indigestion is usually nothing to worry about. Consult your doctor if your discomfort persists for more than two weeks and if you have any of the symptoms:
- Unintentional weight loss or loss of appetite
- Repeated vomiting or vomiting with blood
- Black, tarry stools
- Trouble swallowing that gets progressively worse
- Fatigue or weakness, which may indicate anemia
Symptoms similar to indigestion may be caused by heart attacks. Seek medical attention immediately if you have:
- Shortness of breath, sweating, or chest pain radiating to the jaw, neck or arm
- Chest pain on exertion or with stress
In a nutshell, indigestion is completely normal and most people will certainly experience indigestion in some form throughout their lives. But if you’re unsure or unable to manage indigestion at home, feel free to approach any of our caring pharmacists at Caring Pharmacy for more information on how to deal with your indigestion.
References:
- Minesh Khatri, MD. WebMD.2022. Indigestion. [Online] Available at:https://www.webmd.com/heartburn-gerd/indigestion-overview (Accessed on 8th April 2022)
- Sandy Calhoun Rice. Healthline. 2021. How Do I Have Indigestion? [Online] Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/indigestion#overview (Accessed on 8th April 2022)
- Mayo Clinic. 2022. Indigestion- Diagnosis and Treatments. [Online] Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/indigestion/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352215 (Accessed on 8th April 2022)
- Muneki Igarashi. BMJ Open Gastroenterology. Alteration in the gastric microbiota and its restoration by probiotics in patients with functional dyspepsia. [Online] Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjgast-2017-000144 (Accessed on 8th April 2022)
Latest Health Info
Gut and Skin: How They Are Related?
Did you know that your gut and skin are connected? The gut-skin axis is the relationship between the microorganisms in ...
Ladies, Let’s Bring Out The Beauty In You
Ladies, Let’s Bring Out The Beauty In You As women juggle the demands of work, family, and personal health, taking ...
Healthy Weight, Happy Joints
How Does Weight Affect Knee Health? The Link Between Pounds And Pain Osteoarthritis (OA) involves the degeneration of joints, which ...



