
What Is Osteoarthritis?
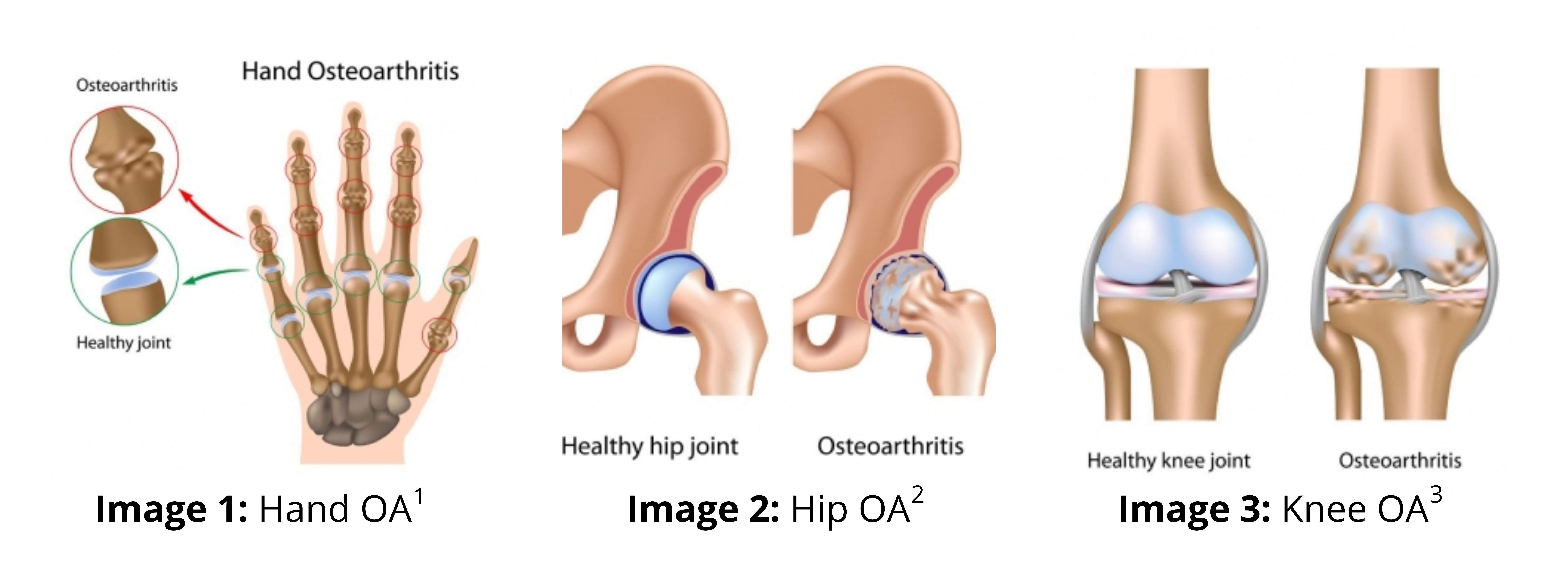
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a joint condition associated with damaged cartilage and joint pain. This condition may get worse over time if left untreated. It can affect the hands, hips and and most commonly – the knees. Symptoms include joint deformity, joint swelling and joint pain.4
How Common Is Knee Osteoarthritis?
Knee OA is common in the elderly. A 2019 study estimated that the prevalence of people suffering from knee osteoarthritis in greater Kuala Lumpur was 30-33%. This study surveyed adults aged 55 years old and above. A difference of prevalence between ethnicity was detected. (Malays: 44.6%, Indians: 31.9%, Chinese: 23.5%).5
Common Risk Factors For Knee Osteoarthritis
The elderly and the female gender are of a higher risk. Being overweight (i.e. Body Mass Index 25-30 kg/m2) as well as a previous knee injury are risk factors of developing knee OA.4
How To Manage Pain?
Medications for Knee OA are associated with pain management. Pain can be measured via the pain score (where 10 is the worst possible pain, and 0 is no pain) (Refer to image 4). To find out more about identifying pain sites and types of pain, you may refer to this infographic.
Medications For Knee Pain
The following are medications that can be used for pain:4
Paracetamol – It is a mild pain reliever. It is generally safe, except for people who have liver failure.
Tramadol – It is a strong pain reliever. It should be used with caution in elderly. The side effects include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, constipation and drowsiness.
NSAIDs – It is a moderate pain reliever, it is able to reduce inflammation as well. This class of medication should be avoided in those with kidney failure. It can be divided into two subclasses with slightly different features:
- (Non-selective COX inhibitors NSAIDs) (e.g. Diclofenac, Naproxen, Ibuprofen) – This class is associated with gastric symptoms, therefore it should be used with caution for those with a history of gastric.
- (Cox-2 inhibitors NSAIDs) (e.g. Celecoxib, Etoricoxib) – This class is associated with cardiovascular
conditions, and should be used in caution if one has a history of a heart attack or stroke. It may be a safer choice if one has an existing gastric condition.
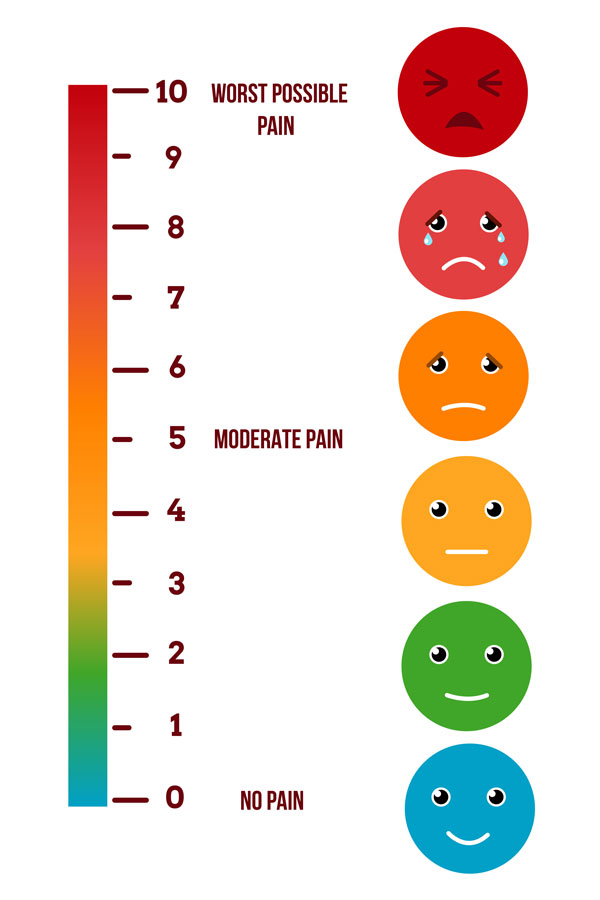
Image 4: Pain score
Supplements For Knee Pain
There are many supplements for knee pain in the market, this article covers only a selected few:
Glucosamine and Chondroitin: Both are components found in the cartilage. It may relieve knee pain, but the effect may only be observed after 3 months.4
Avocado Soybean Unsaponifiables: It has shown to reduce knee pain. Apart from mild gastrointestinal discomfort, it is a safe supplement to take.4
Turmeric: Turmeric is a traditional herb that has multiple functions, one of which is its anti-inflammatory properties. This can be used to reduce inflammation associated with knee OA. It should be taken after food as it may cause mild gastrointestinal discomfort.6
Collagen & Hyaluronic Acid: Collagen is a component found in the cartilage. This helps in the joint repair caused by OA. Hyaluronic acid acts as a lubricant and may increase synovial fluid. Both can work synergistically to reduce knee pain.7
Conclusion
There are many treatments available for knee OA. Apart from the treatments listed above, other treatments include acupuncture, knee guards or support, and surgery. With the wide array for treatment options, there is no need to silently suffer in pain. Do speak to your healthcare provider to find out more and resolve that knee pain! Or you can ask our pharmacists through CARiNG Pharmacy’s Facebook page.
References:
- Hand Osteoarthritis Overview. JJ Ruane. Practical Pain Management. (Web accessed March 2021). Web link: https://www.practicalpainmanagement.com/patient/conditions/osteoarthritis/hand-osteoarthritis-overview
- Hip Osteoarthritis. JJ Ruane, JR Barret. Practical Pain Management. (Web accessed March 2021). Web link: https://www.practicalpainmanagement.com/patient/conditions/osteoarthritis/hip-osteoarthritis/hip-osteoarthritis
- Knee Osteoarthritis Diagnosis. JJ Ruane. Practical Pain Management. (Web accessed March 2021). Web link: https://www.practicalpainmanagement.com/patient/conditions/osteoarthritis/knee-osteoarthritis/knee-osteoarthritis-diagnosis
- Management of Osteoarthritis. Ministry of Health, MOH Malaysia. (2013). Clinical Practice Guidelines.
- Ethnic differences in the prevalence, socioeconomic and health related risk factors of knee pain and osteoarthritis symptoms in older Malaysians. S Mat, M Jaafar, MP Tan, et al. (2019) PLos One.
- The spice for joint inflammation: Anti-inflammatory role of curcumin in treating osteoarthritis. KY Chin (2016) Drug Design, Development and Therapy.
- Effect of an oral preparation containing hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, hydrolyzed collagen type II and hydrolyzed keratin on synovial fluid features and clinical indices in knee osteoarthritis. A pilot study. F Oliviero, R Ramonda, L Punzi, et al. (2020) Reumatismo.
A community awareness message brought to you by:

For more information, visit My Health My Life website or scan this QR code:

Tags
Latest Health Info
Healthy Weight, Happy Joints
How Does Weight Affect Knee Health? The Link Between Pounds And Pain Osteoarthritis (OA) involves the degeneration of joints, which ...
The Gut Warriors: Prebiotics, Probiotics and Postbiotics
When it comes to gut health, you’ve probably heard of prebiotics and probiotics. But did you know there’s also ...
Tip Moreh: Masa Berbuka Puasa
Moreh adalah tradisi unik yang biasanya diadakan selepas solat tarawih pada bulan Ramadan. Ia melibatkan penyediaan dan perkongsian makanan ringan ...




