Monkeypox is an extremely rare disease caused by the monkeypox virus.1 Monkeypox virus belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae. The Orthopoxvirus genus also includes variola virus (which causes smallpox), vaccinia virus (used in the smallpox vaccine), and cowpox virus.2 Monkeypox was first identified in 1958 when two outbreaks of ‘pox-like’ disease occurred in research monkeys.
Monkeypox was first identified in 1958 when two outbreaks of ‘pox-like’ disease occurred in research monkeys.
Symptoms of Monkeypox
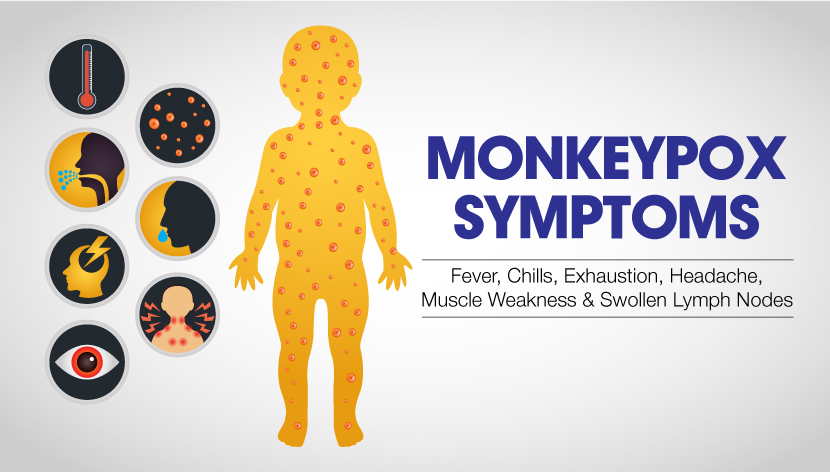 After an incubation period of 7 to 14 days, initial symptoms include fever, chills, exhaustion, headache and muscle weakness.1 This is then followed by swollen lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small, oval shaped organs that are involved in our immune system.
After an incubation period of 7 to 14 days, initial symptoms include fever, chills, exhaustion, headache and muscle weakness.1 This is then followed by swollen lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small, oval shaped organs that are involved in our immune system.
Lymph node swelling distinguishes monkeypox from smallpox as smallpox infection does not involve lymph node swelling.1
After that, widespread rash may occur on the face and body.
The poxes are usually painful and filled with pus. The poxes are usually surrounded by a red circle. The lesions then crust during the healing phase. At this stage, the poxes can be itchy.2
Transmission
Infection can occur through broken skin, mucous membrane (eyes, nose, mouth), respiratory droplets, infected body fluids or even contaminated linen. Transmission from one human to the other mainly occurs via respiratory droplets. Respiratory droplets do not travel far which means transmission via this method requires prolonged face to face contact.2
When the lesions heal, the scabs of the poxes which carry the virus can be inhaled.1
Transmission is mainly through a bite or a contact with animals’ blood, body fluid or cutaneous/mucosal lesions.
Risk of Infection
The risk of infection in Malaysia is low due to the fact that Monkeypox has a low human to human transmission rate.
How to Identify?
If you are exposed to:3
- A suspect, probable or confirmed human case of monkeypox within the incubation period
- Wild, captive or pet mammal from or in the African monkeypox endemic countries within the incubation period
AND
You are having a new skin rash together with one of the following:3
- Fever >38.3 oC
- Intense headache
- Backache
- Myalgia
- Lymph node swelling
- Muscle Cramp
At least at this moment, there is little to worry about monkeypox. Transmission from human to human is low and Monkeypox cases are still relatively low around the world.
References:
- Sandee LaMotte C. What is monkeypox and its signs and symptoms? [Internet]. CNN. 2022 [cited 24 May 2022]. Available from: https://edition.cnn.com/2022/05/19/health/what-is-monkeypox-virus-explainer-wellness/index.html
- Monkeypox [Internet]. cdc.gov. 2022 [cited 24 May 2022]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/index.html
- Muin N. FAQ On MonkeyPox Infection – Info Sihat | Bahagian Pendidikan Kesihatan Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia [Internet]. Infosihat.gov.my. 2022 [cited 24 May 2022]. Available from: https://www.infosihat.gov.my/penerbitan-multimedia/garis-panduan/item/faq-on-monkeypox-infection.html
Tags
Latest Health Info
Brave the Cold: Winter Travel Needs
Winter travel has its kind of magic — snow-covered landscapes, cozy lodges, hot drinks, and festive markets. But traveling in ...
Beat the Heat When Travelling
Whether you’re on a scenic beach vacation or exploring a busy city, hot weather can quickly wear you out and ...
Got Pins & Needles? Learning about Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a common yet serious complication of diabetes, estimated to affect up to 50% of people with the ...




