
Hidden away at home in a drawer or container at home, all of us have expired or unused medication.
While some of us keep expired medication to avoid buying more (you definitely should not), others would rather obey the expiration date stated on the label. Good for you! But the question now is, how should you dispose of them? If your answer is to just throw it in the garbage or flush it down the drain, this article is just for you!
Traces of medicines have been reported in wastewater, ground water, and to a lesser extent, drinking water, with the highest group of medications being painkillers and antibiotics.[1]
So, what is so dangerous about medical waste leaking into our water supply? Let us first talk about its effects on the environment, economy and our health.
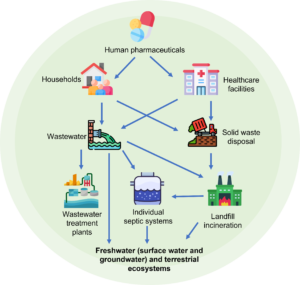
Flowchart of pharmaceutical contamination of groundwater [2]
Discarding your unwanted medicines into the garbage may result in the landfills or sewages leaking these medicines into surface water. Moreover, wastewater treatment does not remove medication residue in the sewerage, resulting in deleterious environmental pollution.
The burden of unused medications
On our PLANET: Risk of global warming and contaminated water
On our ECONOMY: Waste of public resources
On our PEOPLE/ ANIMALS: Health hazard due to accidental ingestion
Now that we know the effects of improper disposal of medical waste, what is the proper way of doing it? Is it complicated and difficult? Do I need a medical degree to do it? IS IT DANGEROUS?!

- Read: Read your medicine labels and check the expiry date
- Remove: Remove expired and unwanted medicines and place them in a bag
- Return: Return all your expired and unwanted medicines to CARiNG Pharmacy

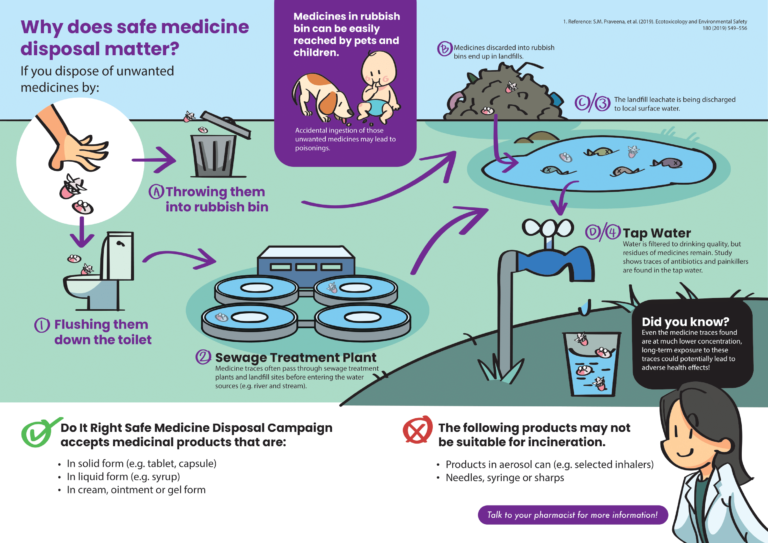
Do drop by any CARiNG Pharmacy to learn more about this greener initiative and how you could participate too.
References:
- Guidelines on The Proper Disposal of Unused Medications. Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya. (Web accessed May 2023). Web link: https://www.um.edu.my/UMique/Sustainability%40UM/UM-Eco-Campus%20Guidelines/02c-guidelines-on-the-proper-disposal-of-unused-medications.pdf
- Pharmaceutical Residues in Freshwater Hazards and Policy Responses. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). (Web accessed May 2023). Web link: https://www.oecd.org/environment/resources/pharmaceutical-residues-in-freshwater-policy-highlights.pdf
- Medical Waste Management. International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC). (Web accessed May 2023). Web link: https://www.icrc.org/en/doc/assets/files/publications/icrc-002-4032.pdf
Latest Health Info
HPV and You: Why Prevention Matters
What is HPV?Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common viral infections affecting both men and women. It spreads ...
Gut and Skin: How They Are Related?
Did you know that your gut and skin are connected? The gut-skin axis is the relationship between the microorganisms in ...
Ladies, Let’s Bring Out The Beauty In You
Ladies, Let’s Bring Out The Beauty In You As women juggle the demands of work, family, and personal health, taking ...




